Mastectomy
Mastectomy is surgery to remove all of the breast tissue. It's used to treat breast cancer or to prevent the tissue from developing into cancer in people at high risk. The most common mastectomies are called simple (or total) mastectomy and modified radical mastectomy. During these procedures, the chest muscle under the breast isn't removed.
Simple (total) mastectomy
During a simple mastectomy, all of the breast tissue (lobules, ducts, and fatty tissue) and the skin, nipple, and areola are removed. This surgery most often requires an overnight hospital stay. Based on the results of surgery and follow-up tests, more treatment may be needed.
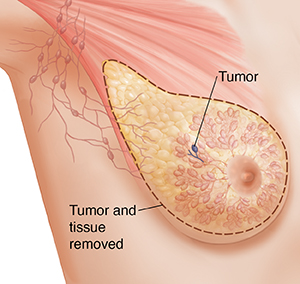 |
| Simple (total) mastectomy. |
Modified radical mastectomy
This type of mastectomy is usually done to treat invasive cancer that has spread to the lymph nodes. All of the breast tissue, skin, nipple, and areola are removed. Some of the lymph nodes in the arm pit are also removed. (These are called the axillary lymph nodes.) The removed nodes are tested for cancer. A surgical drain is often used to keep fluid from building up under the arm pit and the chest wall. This drain usually stays in for a week or two after surgery. This surgery needs an overnight stay in the hospital. Based on the results of the surgery and follow-up tests, more treatment may be needed.
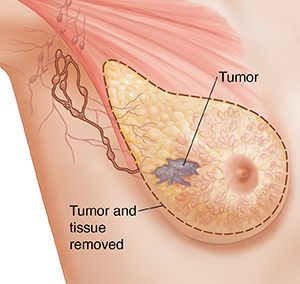 |
| Modified radical mastectomy. |
Right after surgery
You'll wake up in a recovery room. You may have an IV (intravenous) line for fluids and medicines. A tight bandage (dressing) will be wrapped around your chest. There may be a drain coming out of it. Pain medicines will be given to you as needed. A nurse will check your temperature, pulse, and blood pressure. You'll likely stay in the hospital for at least a day.
You'll be given instructions on how to care for the dressing and drains, what kind of pain medicines you should use, and how to take care of yourself as you recover. You'll be given arm exercises to do as you heal. Make sure you understand all the instructions and know when you need to next see your healthcare provider.
Risks and possible complications of mastectomy
Any type of surgery has some risk. Risks for mastectomy include:
-
Pain or numbness
-
Bleeding
-
Infection
-
Swelling at the surgery site
-
Shoulder stiffness
-
Fluid collection (seroma) in the area where the cancer was removed
-
Blood collection (hematoma) in the area where the cancer was removed
-
Long-term swelling of the hand, arm, arm pit, and chest (lymphedema)
-
Nerve damage that can cause numbness
-
Wound-healing problems and scarring
Talk with your healthcare provider about the risks related to your surgery and what you can do to help prevent problems.
When to call your healthcare provider
Talk to your provider about problems you should watch for. Call them right away if you have any of the following after surgery:
-
Fever of 100.4°F (38°C) or higher, or as advised by your provider
-
Chills
-
A change in the way the drainage looks or drainage soaks the dressing
-
Incision opens up or the edges pull apart
-
The surgical drain tubing (if you have one) falls out of the chest wall or under arm
-
Signs of infection around the incision, such as redness, drainage, warmth, and increased pain
-
Cough or shortness of breath
-
Trouble passing urine or changes in how your urine looks or smells
-
Swelling in your hand, arm, or chest that gets worse or isn't getting better a week or two after surgery
-
Pain, redness, swelling, or warmth in an arm or leg
-
Any unusual bleeding or bleeding that soaks the dressing
-
Any other problems your provider told you to watch for and report
Make sure you know how to reach your healthcare provider in case problems come up. Know what number to call with questions or problems after office hours, on weekends, and on holidays.
Online Medical Reviewer:
Jessica Gotwals RN BSN MPH
Online Medical Reviewer:
Susan K. Dempsey-Walls RN
Online Medical Reviewer:
Todd Campbell MD
Date Last Reviewed:
8/1/2023
© 2000-2025 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.